Rising Prices, Rising Challenges: Navigating Fuel Costs in Ethiopian Gas Stations
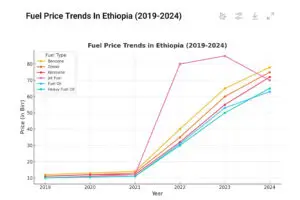
Fuel prices are a central concern for gas station owners, operators, and consumers across Ethiopia. As a country that imports the majority of its petroleum products, Ethiopia is highly sensitive to global oil price fluctuations, foreign exchange availability, and government-imposed pricing regulations. This article explores the challenges gas station businesses face due to rising fuel costs, their impact on the broader economy, and strategies that station owners can adopt to navigate these challenges.
1. Understanding the Drivers of Rising Fuel Costs in Ethiopia
Fuel price increases in Ethiopia are often driven by a combination of global and domestic factors. These include:
Global Oil Price Volatility: As a net importer of petroleum, Ethiopia’s fuel costs are directly influenced by fluctuations in international oil prices. Events such as geopolitical tensions, supply disruptions, or changes in production levels by major oil-exporting countries can lead to price surges.
Exchange Rate Challenges: Ethiopia’s reliance on imported fuel means that exchange rate fluctuations have a significant impact on fuel prices. A weakening Ethiopian birr increases the cost of purchasing fuel on international markets, which is passed down to consumers.
Government Policy: While the Ethiopian government regulates fuel prices to protect consumers, adjustments are periodically made to reflect global market trends. These price hikes can strain consumers and gas station operators alike.
Transportation Costs: As a landlocked country, Ethiopia incurs additional transportation costs for importing fuel through neighboring ports, such as Djibouti. These costs can rise with increasing global shipping rates or regional logistical issues.
2. The Impact of Rising Fuel Prices on Gas Station Operations
Rising fuel prices present significant challenges for gas station owners and operators. Some of the key issues include:
Reduced Profit Margins: Ethiopian gas station operators often work with fixed profit margins determined by the government. When fuel costs rise, operating expenses such as transportation and electricity increase, but retail margins remain the same, squeezing profits.
Decreased Consumer Spending: Higher fuel prices can lead to reduced consumer demand. Drivers may limit their fuel purchases, and businesses that rely on fuel may cut back, reducing overall sales for gas stations.
Increased Competition: Rising prices may lead to heightened competition among gas stations as consumers shop around for better prices or switch to alternative fuel types, such as kerosene or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG).
Operational Challenges: Frequent price adjustments require gas stations to update their systems and ensure accurate pricing on dispensers, which can increase administrative burdens.
3. Broader Economic Effects of Rising Fuel Costs
The ripple effects of rising fuel prices extend beyond gas station operations, affecting Ethiopia’s economy in the following ways:
Transportation Costs: Higher fuel prices drive up the cost of transportation for goods and people, contributing to inflation across various sectors, including food, construction, and manufacturing.
Impact on Agriculture: Farmers, who rely heavily on fuel for irrigation pumps and transportation, face increased costs that can lead to higher food prices and reduced agricultural output.
Energy Access: Rising fuel prices make it more expensive to run generators, which many businesses and households rely on due to inconsistent electricity supply.
4. Strategies for Gas Station Owners to Navigate Rising Fuel Prices
Despite these challenges, gas station owners and managers can take proactive steps to mitigate the impact of rising fuel costs:
Invest in Efficiency: Upgrading fuel dispensers and storage systems to minimize wastage or leaks can help reduce operating costs. Automated tank monitoring systems can improve inventory management and prevent losses.
Explore Diversification: Gas stations can diversify their revenue streams by offering additional services such as convenience stores, car washes, or repair shops. These services can help offset declining fuel sales.
Leverage Technology: Adopting digital tools, such as remote price adjustment systems or mobile payment platforms, can streamline operations and improve customer convenience.
Collaborate with Suppliers: Building strong relationships with fuel suppliers can provide more stable pricing or priority access during supply shortages.
Educate Customers: Gas station owners can offer tips to customers on improving fuel efficiency, such as proper tire inflation or avoiding excessive idling. This builds customer loyalty and positions the station as a trusted partner.
5. Government Support and Policy Recommendations
To support gas station operators and mitigate the effects of rising fuel costs, the Ethiopian government can consider the following measures:
Adjust Profit Margins: Allowing gas station operators to adjust margins periodically to reflect rising operating costs can help maintain business viability.
Subsidies for Critical Sectors: Targeted fuel subsidies for public transportation, agriculture, and essential services can alleviate some of the economic pressures caused by price increases.
Infrastructure Development: Investing in better fuel storage and distribution networks can reduce transportation costs and improve supply reliability.
Promoting Alternative Energy: Encouraging the use of renewable energy solutions, such as solar-powered stations or electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, can reduce reliance on imported fuel in the long term.
Conclusion
Rising fuel prices present significant challenges for Ethiopia’s gas station businesses, impacting profitability, consumer behavior, and overall economic activity. However, by adopting innovative strategies, leveraging technology, and working closely with the government, gas station operators can navigate these challenges and build more resilient businesses. As Ethiopia continues to develop its energy and transportation sectors, a collaborative approach will be essential to ensuring that gas stations remain a vital part of the country’s economy.
Do you operate a gas station? You can use Gas Pro, the first gas station management software in Ethiopia, to get these benefits:
Automated Tank Monitoring
Using Gas Pro, you can automatically measure your tank at the press of a button. This saves you time while increasing your measurement accuracy
Real-Time Fuel Level Alerts
Gas Pro will give “low fuel alerts” when the fuel reaches critical level and “fuel tank full” alerts when they fill up. This enables gas station owners and managers to coordinate supply of fuel.
Theft and Loss Prevention
Gas Pro’s dual-level sensors detect theft or tampering, reducing financial losses. Accurate records of fuel deliveries prevent disputes with suppliers.
Remote Pricing Control
Gas Pro enables you to remotely adjust the prices on your gas pumps thus increasing your ability to react to price changes made by the government.
More Stories

Operational Inefficiencies in the Ethiopian Gas Station Industry
Manual dipstick measurements and inventory tracking are labor-intensive, error-prone, and time-consuming. These methods often result in inventory discrepancies, which can lead to financial losses and operational disruptions.

Keeping the Pumps Running: Tackling Supply Chain Challenges in Ethiopia’s Fuel Market
Fuel is the lifeblood of any economy, powering everything from transportation and agriculture to industrial production. In Ethiopia, a nation undergoing rapid growth and development, the demand for fuel is rising steadily. Yet, ensuring a consistent and affordable fuel supply remains a formidable challenge.

From Addis to Rural Ethiopia: Bridging the Fuel Access Gap
Bridging the fuel access gap between Addis Ababa and rural Ethiopia will require concerted efforts from all stakeholders, from government officials to private investors. With the right policies, infrastructure investment, and technological innovation, Ethiopia can ensure that all its citizens—regardless of where they live—have equal access to the fuel they

The Future of Fuel: Opportunities and Growth in Ethiopia’s Gas Station Market
Ethiopia’s gas station market is at the cusp of transformation, and for those looking to invest, the future offers plenty of opportunities to drive growth and innovation. Whether you’re an entrepreneur looking to build your brand or an investor seeking profitable ventures, this is a sector worth watching.
Rising Prices, Rising Challenges: Navigating Fuel Costs in Ethiopian Gas Stations
Fuel prices are a central concern for gas station owners, operators, and consumers across Ethiopia. As a country that imports the majority of its petroleum products, Ethiopia is highly sensitive to global oil price fluctuations, foreign exchange availability, and government-imposed pricing regulations.

Fueling Ethiopia: How Government Policies Shape the Gas Station Industry
The gas station business in Ethiopia plays a pivotal role in keeping the country’s economy moving. From fueling vehicles to powering machinery, the availability and pricing of fuel impact everything from transportation costs to consumer goods.
